Knee injuries come in various forms, each with its own consequences due to the intricate makeup of the knee joint—comprising bones, cartilage, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and soft tissues. While swelling often signals an injury, the outcome of treatment for a swollen knee and its healing depends on the specific type of injury that made the knee swell. Seek expert evaluation and effective treatment from the pain management professionals at Pro Spine & Pain. With five locations throughout Wisconsin, at Kenosha, Waukesha, Layton, Franklin, and Madison, one of our compassionate doctors will work with you to resolve your knee injury fast.
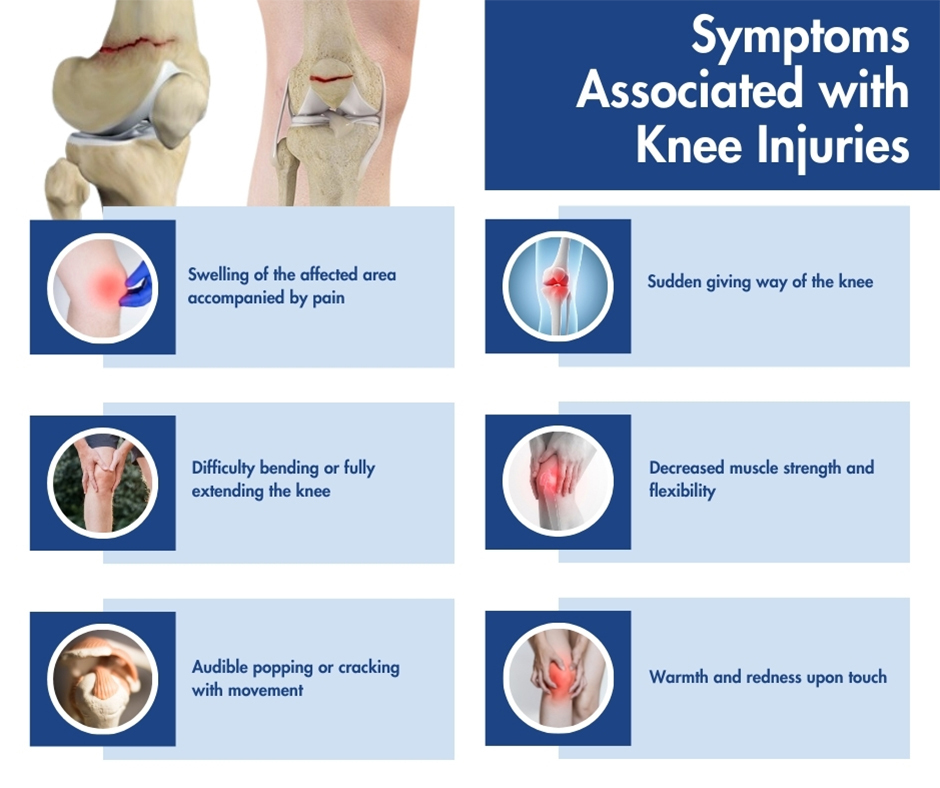
Symptoms Associated with Knee Injuries
These injuries can stem from increased strain on the knees through a wide range of normal activities, like carrying a lot of weight or playing sports or normal wear and tear, making knee injuries more probable as you age. Actions ranging from aerobic dance to casual basketball can lead to painful torn tendons or ligaments from a sudden leg twist. Knee pain and swelling typically arise from this type of cartilage or joint damage.
Signs of knee injury include:
- Swelling of the affected area accompanied by pain
- Difficulty bending or fully extending the knee
- Audible popping or cracking with movement
- Sudden giving way of the knee
- Decreased muscle strength and flexibility
- Warmth and redness upon touch
Common Causes of Knee Pain
Knee injuries can arise from various sources, such as direct impact, gradual wear and tear, or an awkward twisting motion. But certain conditions can weaken the knee, making it more vulnerable and increasing the chances of it being injured.
Factors that can increase the likelihood of knee injuries include:
- Excess Weight: Being overweight places added strain on the knees, particularly during activities like stair climbing. Muscles may become less flexible and lose strength with excess weight, leading to instability and a higher risk of injury.
- Participating in Sports: Engaging in sports activities involving jumping, bending, kicking, and twisting can stress the knees, especially if done excessively or after a period of inactivity. Some sports, like running and jogging, pose particular challenges to knee health leading to sports injuries.
- Occupational Hazards: Certain professions can take a toll on the knees, particularly if they involve heavy lifting or frequent squatting or kneeling. Tasks such as carrying heavy objects over long distances, scrubbing floors, or gardening can lead to knee problems and injuries.
- Other Factors: Wearing inappropriate footwear for specific activities increases the chances of knee injuries, whether it’s during sports, exercise, or household chores. Furthermore, a cartilage defect can impede the normal function of the joint.
Risk Factors for Knee Injuries
Knee injuries pose a widespread concern across all age groups and activity levels. Whether you’re an athlete, fitness enthusiast, or simply prioritize knee health, understanding risk factors will help you prevent damaging your knees and help with long-term protection.
- Age-Related Issues: Aging brings natural joint wear and tear, elevating the risk of knee injuries due to factors like decreased cartilage density, flexibility, muscle strength, and slower healing. Older individuals should focus on maintaining joint health through suitable exercise and lifestyle adjustments and ensure any knee pain is investigated promptly, particularly for arthritis of the knee.
- Overuse: Repetitive, high-stress activities can cause overuse injuries like tendonitis or bursitis, commonly seen in runners, cyclists, and dancers. Managing intensity, incorporating rest days, using proper gear, and cross-training can help mitigate this risk.
- Improper Technique: Incorrect form in physical activities, like weightlifting or sports, increases the chance of injuring the knees, as does wearing inappropriate footwear during strenuous activity. Utilizing proper mechanics is vital for activities involving twisting or abrupt movements.
- Muscle Imbalances: Imbalances in muscle strength around the knee, caused by inadequate training, can lead to instability and injury. Balanced exercises targeting all muscle groups surrounding the knee are important for strength and stability.
- Previous Injuries: Past knee injuries weaken joint stability, making reinjury more likely. Proper rehabilitation and strengthening exercises prescribed by healthcare professionals will minimize this risk.
Injuries that Cause a Swollen Knee
If you have a swollen knee, chances are you have a knee injury, as that is a very common symptom. Book a prompt consultation with a specialist at Pro Spine & Pain in Wisconsin for a thorough examination and personalized knee injury swelling treatment plan designed to address your specific problems.
Common knee injuries include:
- Fracture: Resulting from falls, car accidents, sports impacts, or weakened bones due to conditions like osteoporosis.
- Strained or Sprained Knee: Overexertion during physical activity without adequate preparation can cause knee sprains and strains. These conditions occur when the ligaments, tendons, or muscles are overstretched or torn.
- Meniscal Damage: Sudden twists can tear the knee joint’s cartilage, known as the meniscus.
- Knee Cartilage Damage: Knee cartilage injuries cause pain, inflammation, clicking, catching, and limited motion. Larger injuries may worsen, potentially leading to osteoarthritis.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Damage to the kneecap and surrounding cartilage causes this pain.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injury: Cruciate ligament tears are not rare and ACL injury commonly occurs during sudden changes in direction, prevalent in sports like soccer.
- Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Injury: Another of the main ligaments that connect the thigh bone to the shin bone, the PCL can be injured by direct hits, such as football tackles.
- Medial Cruciate Ligament (MCL) Injury: Direct blows to the outside of the knee can damage the MCL.
- Damage to Collateral Ligaments: Collateral ligaments maintain knee stability by preventing excessive sideways movement. Injury can result from a forceful impact or a twisting motion on the inside or outside of the knee.
- Patellar Tendonitis: Protecting the knee’s range of motion, the patellar tendon can become irritated and inflamed, a condition often seen in athletes engaging in running, jumping, skiing, or cycling.
- Knee Bursitis: Damage to fluid-filled bursae causes friction between bones and surrounding tissues, disrupting joint function.
- Loose Bodies: Bone fragments or bits of articular cartilage from injury or accidents can impede knee joint movement.
- Osgood-Schlatter Disease: Inflammation of the patellar tendon, typically affecting preteen and teenage boys, can lead to tendon tears.
- Dislocated Kneecap: Shifting of the kneecap out of place results in pain and discomfort.
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome: Tightening of the iliotibial band causes sharp, burning pain by irritating the thigh bone.
- Plica Syndrome: Irritation of synovial tissue bands due to overuse or injury leads to pain and discomfort.
Treatment for Knee Injuries
Based on your diagnosis, your Wisconsin pain management specialist offers several knee injury treatment options. Swollen knee treatment normally includes rest, applying ice to the injury to reduce swelling, and elevating the knee above heart level. Immobilizing the knee with a brace can provide support and prevent further strain.
Your doctor will give you a thorough examination and record your medical history. You may also be recommended for further investigation, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). They may then suggest pain relievers like ibuprofen or prescribe stronger medication for intense pain. Physical therapy can aid in muscle strengthening and improving knee joint mobility. Cartilage injury knee treatment may include rest, ice, and over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs to lessen swelling. In cases of severe cartilage damage, fractures, or ligament damage, surgical interventions such as total joint replacement may be necessary, although surgery is normally considered a last resort.
For personalized advice and consultation, contact your pain management professional at Pro Spine & Pain for the best non-surgical solution.

