We’re pleased to announce that Pain Physicians of Wisconsin is now Pro Spine Pain.
We’re pleased to announce that Pain Physicians of Wisconsin is now Pro Spine Pain.
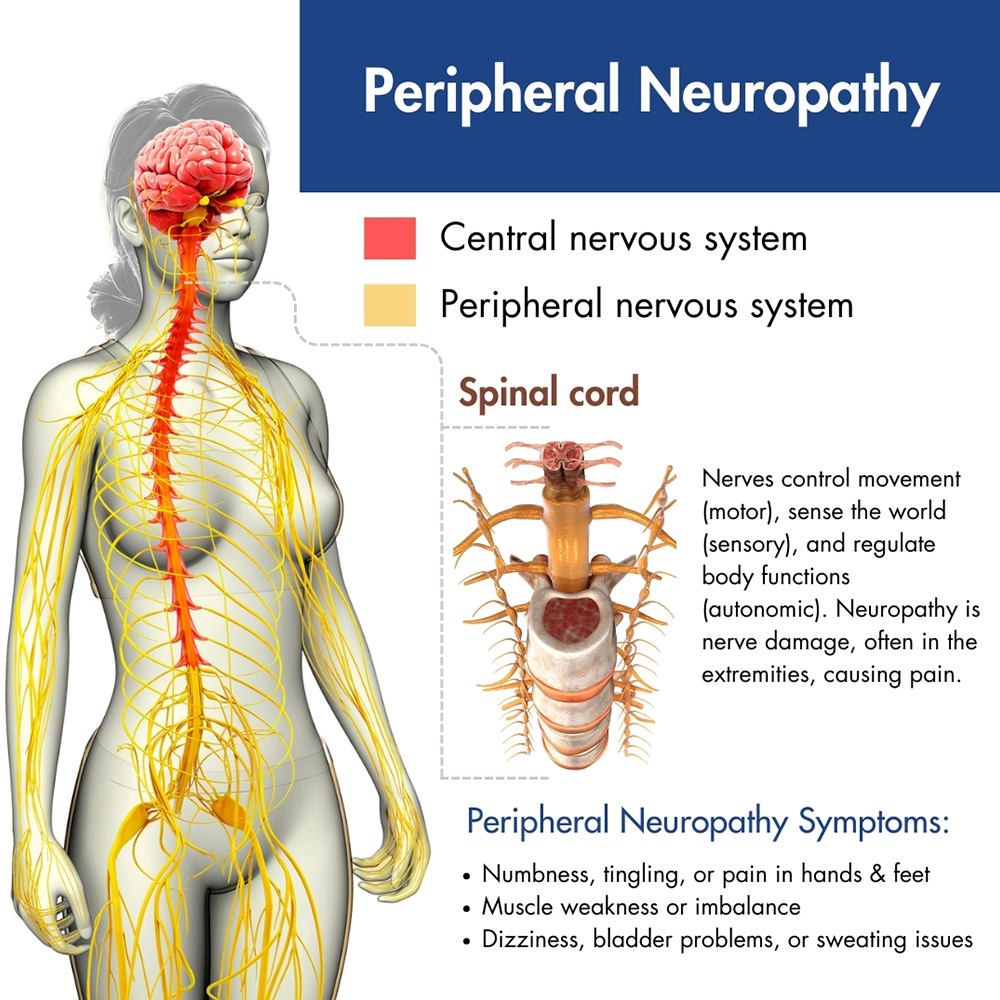 Neuropathy, and especially peripheral neuropathy, refers to the transmission of abnormal signals from nerves throughout the body to the brain, resulting in pain. For a thorough diagnosis and specialized care, turn to the pain management experts at Pro Spine & Pain in Wisconsin. Whether you require treatment for problems with your feet due to diabetes or seek relief from peripheral neuropathy, trust the expertise of our pain specialists at five locations: Kenosha, Waukesha, Layton, Franklin, and Madison. Don’t endure unnecessary suffering; contact your nearest pain clinic today for swift assistance so that you’re feeling better fast.
Neuropathy, and especially peripheral neuropathy, refers to the transmission of abnormal signals from nerves throughout the body to the brain, resulting in pain. For a thorough diagnosis and specialized care, turn to the pain management experts at Pro Spine & Pain in Wisconsin. Whether you require treatment for problems with your feet due to diabetes or seek relief from peripheral neuropathy, trust the expertise of our pain specialists at five locations: Kenosha, Waukesha, Layton, Franklin, and Madison. Don’t endure unnecessary suffering; contact your nearest pain clinic today for swift assistance so that you’re feeling better fast.
Neuropathy is a complex condition that results from nerve damage throughout the nervous system. It can occur due to various factors, including injuries or medical conditions like pinched nerves.
The nervous system comprises two primary components:
Motor nerves regulate muscle movement, sensory nerves monitor sensory input, and autonomic nerves control unconscious activities such as breathing. Because it affects the peripheral nervous system, neuropathy is also known as peripheral neuropathy or diabetic nerve pain. It arises from damage to the nervous system.
Different types of neuropathies exist, including mononeuropathy affecting a single nerve type like carpal tunnel syndrome, multifocal neuropathy impacting nerves in a specific area like proximal neuropathy affecting the hip, buttock, or thigh, and polyneuropathy involving nerves across multiple areas of the body. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment approaches.
Peripheral neuropathy commonly manifests as numbness or discomfort along the nerve pathways in the hands or feet, often referred to as neuralgia. However, some individuals may experience symptoms in other parts of their body as well.
Different types of peripheral neuropathy present distinct symptoms, including:
If you recognize any of these symptoms, we recommend seeking evaluation from one of the Wisconsin pain professionals at Pro Spine & Pain. Our comprehensive approach will work to identify and address the underlying cause of your pain, whether it is acute or chronic, enabling you to regain a pain-free lifestyle and get back to your normal day-to-day activities.
Neuropathy, although occasionally hereditary, is predominantly associated with underlying neurological or health conditions, or nerve damage.
Various factors contribute to the development of peripheral neuropathy, including:
Neuropathy treatment starts with diagnosis. At Pro Spine & Pain in WI, pain management specialists conduct comprehensive evaluations and employ various tests and investigations to accurately diagnose the specific type of peripheral neuropathy. In addition to blood tests, MRI scans, neurological examinations, and other procedures, we employ state-of-the-art medical technology to support the diagnostic process and subsequent treatment planning.
An estimated 20 million Americans are affected by this condition, and it can have sometimes debilitating consequences on the day-to-day life of those living with it.
Some of the problems caused by neuropathy include:
For these reasons, early diagnosis and intervention is crucial to managing symptoms and maintaining good quality of life. Our expert pain management team are dedicated to meticulously identifying the underlying cause of your neuropathy and crafting a tailored treatment plan designed to provide optimal relief and support.
The objective of treatment for peripheral neuropathy is twofold: managing the underlying condition responsible for neuropathy and alleviating associated symptoms. In cases where no underlying cause is identified, healthcare providers may adopt a strategy of observing the condition over time coupled with home remedies to assess symptom relief. However, when an underlying condition is present, peripheral neuropathy treatment plans may encompass various approaches, including medication, physical therapy, medical devices, nerve blocks, nerve stimulation (neuromodulation), and surgery as a last resort.
Medications play a key role in managing neuropathic pain, with options ranging from over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers to anti-seizure medications, topical treatments, or antidepressants. Physical therapy is often recommended to enhance muscle strength and flexibility, while medical devices such as braces, canes, walkers, or wheelchairs may aid in mobility and support.
Nerve blocks involve the targeted placement of diagnostic and therapeutic medication near affected nerves to diminish pain transmission, while nerve stimulation (neuromodulation) works to modulate pain signals before they reach the brain.
Although surgery is typically considered only if other remedies are unsuccessful, it may be necessary in cases where pressure on nerves needs to be relieved.
Before turning to more invasive treatments, lifestyle modifications are often recommended to alleviate neuropathy symptoms, particularly in the legs and feet. These changes include foot care practices such as daily inspections for blisters, cuts, or calluses, regular exercise to reduce pain and improve muscle strength, quitting smoking to maximize blood flow, adopting a nutritious diet, decreasing alcohol consumption, managing blood glucose levels (especially for people with diabetes), ensuring a clutter-free environment to prevent falls, and reviewing current medications with a healthcare provider to mitigate potential adverse effects.
Prompt medical attention is essential if unusual tingling, weakness, or neuropathic pain is experienced in the hands or feet, as early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for symptom control and preventing further peripheral nerve damage. Individuals seeking comprehensive neuropathy care can contact Pro Spine & Pain for a consultation to explore treatment options tailored to their needs.

Thomas Stauss, MD, completed both his undergraduate and medical studies at the esteemed University of Wisconsin in Madison. Dr. Stauss values having access to a wide array of cutting-edge treatment options, ensuring effective relief for his patients' discomfort and a significant enhancement in their quality of life. More specifically, he specializes in utilizing implanted devices to manage chronic pain. Dr. Stauss’s primary objective is to uphold the dignity of each patient while delivering ethical and professional services.
More about Dr. Stauss