We’re pleased to announce that Pain Physicians of Wisconsin is now Pro Spine Pain.
We’re pleased to announce that Pain Physicians of Wisconsin is now Pro Spine Pain.
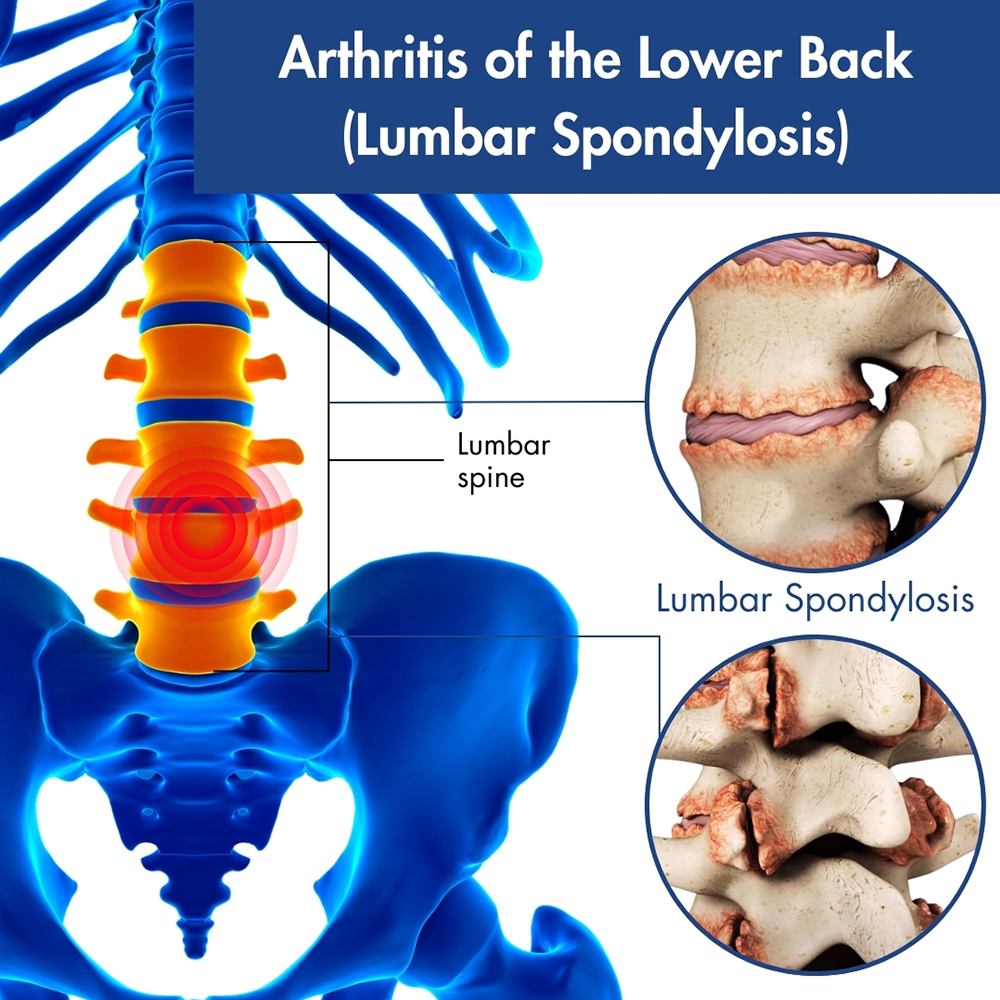 Arthritis of the back, also known as spinal arthritis or spondylosis, is a common condition characterized by the inflammation, degeneration, and eventual breakdown of the joints and discs in the spine. It can cause significant pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, impacting the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
Arthritis of the back, also known as spinal arthritis or spondylosis, is a common condition characterized by the inflammation, degeneration, and eventual breakdown of the joints and discs in the spine. It can cause significant pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility, impacting the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.
The spine is a complex structure made up of vertebrae, discs, nerves, and muscles, all working together to provide support, stability, and flexibility to the body. Arthritis of the back typically affects the facet joints, which are small joints located between each vertebra, as well as the intervertebral discs, which act as shock-absorbing tissue between the vertebrae.
There are several types of arthritis that can affect the spine, with the most common being osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis, each with its own unique characteristics and symptoms.
Spondylosis or spinal osteoarthritis is a degenerative disorder that might lead to a loss of normal spinal structure and function.
The degenerative process involved in this condition may affect the following regions:
Arthritis of the back can manifest with a variety of symptoms, often varying in severity depending on the type and progression of the condition. The pain may be localized to the back or may radiate to other parts of the body, such as the hips, legs, or arms.
Common symptoms of lumbar arthritis include:
The exact cause of arthritis of the back is not fully understood, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development, including age, genetics, injury, obesity, and repetitive stress on the spine. As people age, the cartilage in the spine naturally begins to deteriorate, increasing the risk of developing arthritis.
As you grow older, natural degenerative changes occur in your spine. Even if you lead a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and proper nutrition, these changes still progress over time, impacting your spine.
One effect is the dehydration of vertebral discs, weakening them. This weakening allows facet joints to move closer together, causing cartilage damage. These joints are crucial for enabling the free movement and rotation of your back, so when the cartilage around them breaks down, it leads to stiffness and restricted motion as side effects. As cartilage wears away completely, bones start rubbing against each other, prompting the growth of new bone, known as bone spurs, within the facet joints. This process results in stenosis, the narrowing of the space through which nerve roots pass, ultimately causing intense pain.
These degenerative changes highlight the importance of proactive measures to maintain spinal health and mitigate the progression of such conditions as you age. Regular exercise, maintaining proper posture, weight loss, if necessary, and seeking medical advice for managing symptoms are essential steps in preserving spine health and overall well-being. The pain management specialists at Pro Spine & Pain will work with you to develop a plan to manage your symptoms and get back to your best.
Lumbar spondylosis is typically caused by a combination of factors, including age-related changes, genetics, injury, and lifestyle factors. As people age, the cartilage that cushions the joints in the spine naturally begins to deteriorate, leading to the development of arthritis. This wear and tear process is known as osteoarthritis, the most common form of arthritis in the back.
Genetics also play a role, as certain genes have been linked to an increased susceptibility to developing arthritis. Additionally, obesity and repetitive stress on the spine from activities such as heavy lifting or poor posture can accelerate the degenerative process.
Injuries to the spine, such as fractures, dislocations, or repetitive stress injuries, can also damage the joints and surrounding tissues, accelerating the degenerative process and increasing the risk of developing arthritis later in life.
Lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor posture, and repetitive movements that strain the spine can also contribute to the development of back arthritis by placing excessive stress on the joints and accelerating wear and tear.
Some people with psoriasis develop a specific type of lower back spondylosis known as psoriatic arthritis. It can affect joints on one or both sides of the body. People with psoriatic arthritis often suffer signs and symptoms similar to those of rheumatoid arthritis.
Diagnosing arthritis in the back typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, including a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. During the physical examination, your doctor may assess range of motion, joint tenderness, and neurological function. Imaging studies such as X-rays, MRI, or CT scans may be ordered to visualize the extent of joint damage, identify bone spurs, or assess the condition of the surrounding tissues.
Once diagnosed, treatment for arthritis in the back aims to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. This often involves a combination of conservative therapies and lifestyle modifications.
The choice of treatment depends on your symptoms, the severity of your condition, and your overall health goals. For this reason, you should discuss your symptoms thoroughly with your doctor.
Arthritis of the lower back is a complex and often debilitating condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. With symptoms ranging from persistent pain and stiffness to reduced mobility and nerve compression, it can significantly impact one’s quality of life. However, with early diagnosis, appropriate medical management, lifestyle modifications, and supportive interventions, individuals with arthritis of the back can effectively manage their symptoms and maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle. Ongoing research into the causes, treatments, and prevention strategies for arthritis in the back holds promise for improving outcomes and enhancing the well-being of those affected by this condition.
Get help for the symptoms of arthritis in the back as soon as possible. Back pain relief will enable you to do all the things you love so you can live life to the fullest. Contact Pro Spine & Pain today to set up a consultation and discover the best non-surgical treatment for lumbar spondylosis and receive a comprehensive treatment plan to manage pain. Choose from five locations in Wisconsin in Kenosha, Waukesha, Layton, Franklin, or Madison.

Thomas Stauss, MD, completed both his undergraduate and medical studies at the esteemed University of Wisconsin in Madison. Dr. Stauss values having access to a wide array of cutting-edge treatment options, ensuring effective relief for his patients' discomfort and a significant enhancement in their quality of life. More specifically, he specializes in utilizing implanted devices to manage chronic pain. Dr. Stauss’s primary objective is to uphold the dignity of each patient while delivering ethical and professional services.
More about Dr. Stauss